An equation containing at least one derivative of a dependent variable with respect to an independent variable Differential equation means and example such that
y d y/d x +2x = 0 …………………………………….a
x d ²y / d x² + d y / d x – 2 x = 0………………………b
is called Equation (a) and Equation (b) a differential equation.
Derivatives may be of first or higher orders. A differential equation containing only the derivative of first order can be written in terms of differential.
So we can write equation (a) y d y +2x d x = 0
But equation (b) cannot be written in the form of differential.
Order of differential equation:
The highest derivative in the equation is called order of a differential equation.
First order differential equation:
The form of the Equation (a) is called FIRST order differential Equation.
Second order differential equation:
The form of the Equation (b) is called SECOND order differential Equation
Differential equation means and example of first order:
EXAMPLE:
Consider the equation
y = A x ² +4……………………… A
Where A is the real constant
Differentiating Equation A with respect to x gives
d y / d x = 2 A x…………………… B
Equation A can be written as A = y – 4 / x ² this value putting in Equation B.
d. y / d x = 2 (y – 4 / x ²) x
⇒ x d y / d x = 2 y – 8
⇒ 2 y – x d y / d x = 8…………………….. C
Substituting the value of y and its derivative in C. we see that it is satisfied.
2 (Ax ² + 4) – x (2 A x)
= 2 A x ² +8 – 2 A x ²
= 8
Which shows that Equation A is a solution of Equation C.
Giving a particular value to A, say A = – 1 we get
y = – x ² + 4
WE CHECK EQUATION C
putting y = – x ² + 4 and its derivative
d y / d x = -2 x
so y = – x ²+ 4 is also a derivative of C.
For different value of A on differential equation C:
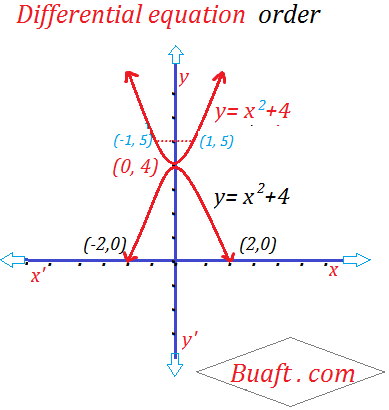
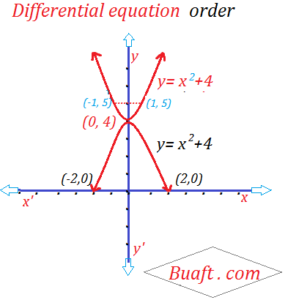
By putting different value of A. we get the different parabola with vertex at (0, 4) and the Axis along the y-axis. We have drawn two members of parabolas
y = A x ² + 4 for A = – 1, 1
All solution obtained from Equation A by putting different value of A, are called the particular solution of Equation C. While the solution C Itself is called the general solution of C.
A solution of a differential equation is a relation between the variable (not involving the derivative)Which satisfied the differential Equation.
We shall solve a differential Equation of first order with variables separable in the form.
d. y / d x = f (x) / g (y) or d y / d x = g(x) / f(x)
RELATED POST:
- Limit of a function concept
- ♣
- Left-hand limit and right-hand limit
- ♣
- Cube root of unity power
- ♣
- Addition and multiplication laws of real number
- ♣
- table of standard ellipse
- ♣
- standard equation of hyperbola math
- ♣
- ellipse in standard form concept
- ♣
- 3.14159 is rational or irrational