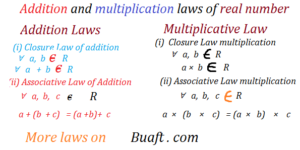
Addition and multiplication laws of real number
(1) Addition Laws of real number
(i) Closure Law of addition
∀ a, b ∈ R (for all a, b is a part of real number)
such that
∀ a + b ∈ R (for all a + b is a part of real number)
(ii) Associative Law of Addition
∀ a, b, c ∈ R (for all a, b, c is a part of real number)
Such that
a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c
(iii) Additive identity
∀ a ∈ R And ∃ (there exist) 0 ∈ R
Such that
a +0 = 0 + a = a
(iv) Additive Inverse
∀ a ∈ R And ∃ (there exist) – a ∈ R
Such That
a + (-a) = 0 = (- a) + a
(v) commutative Law of Addition
∀ a, b ∈ R (for all a, b is a part of real number)
Such that
a + b = b + a
Addition and multiplication laws of real number
(2) Multiplicative Law of Real number
(i) Closure Law multiplication
∀ a, b ∈ R (for all a, b “is a part” of real number)
a × b ∈ R
(ii) Associative Law multiplication
∀ a, b, c ∈ R (for all a, b, c is a “part” of real number)
Such that
a × (b × c) = (a × b) × c
(iii) Multiplicative Identity
∀ a ∈ R And ∃ (there exist) 1 ∈ R
Such that
a × 1 = 1 × a = a
1 is called the multiplicative identity of real number
(iv) multiplicative Inverse
∀ a (≠ 0) ∈ R And ∃ (there exist) a ‾¹ ∈ R
Such That
a × a ‾¹ = a ‾¹ × a = 1 (a ‾¹ is also written as 1 / a)
(v) Commutative law of multiplication
∀ a, b ∈ R (for all a, b is a part of real number)
Such that
a × b = b × a
RELATED POST
- Addition law of multiplication of real number
- ♠
- Roster or tabular form of set
- ♣
- properties of determinant proves
- ♥
- proper and improper subset example
- ♣
- Type of surd or irrational root definition and example
- ♣
- commutative property of rational number
- ♣
- power of iota
- ♣
- 3.14159 is rational or irrational